
How to get started on Flipped classroom in the digital space for our teachers
Are you a teacher seek to be more effective on the virtual space as COVID forces us onto the internet? As I was looking for other educational tools, I found the flipped classroom concept really interesting or even kinda radical. As technology evolves and become more integrated with our lives, we have to find ways to leverage on the strengths of technology to enable us to do more with less. For example, to reach out to more students with less time. Teach more concepts with less classroom time. Have you heard of flipped classroom and what does it mean? We will find out today!
Here’s a video I find really descriptive to help you kickstart your understanding of this pedagogical approach:
In this article, we will be going through the following sections:
- What is Flipped classroom?
- What is technology’s role?
- Benefits of Flipped classroom
- How to get started?
- Challenges of flipped classroom
- Alternatives - What are you solving?
Before we begin, I would like to give a shout out to exploreily for putting together insightful and meaningful articles across many blogs across the world. I’m also featured in their blog as well, so check them out!
Lets dive in first to understand what is Flipped classroom.
#1. What is Flipped classroom?
The flipped classroom pedagogical approach has two key spaces: the group space which we know as the classroom, and the individual learning space which is student’s personal time outside of classroom.
Flipped classroom essentially moves the group learning such as content teaching from classrooms to their own individual learning space aka outside of classroom. Once that content teaching is done outside of the classroom, your classroom time can now be transformed into a dynamic, interactive learning environment which students can engage these learnt concepts creatively.
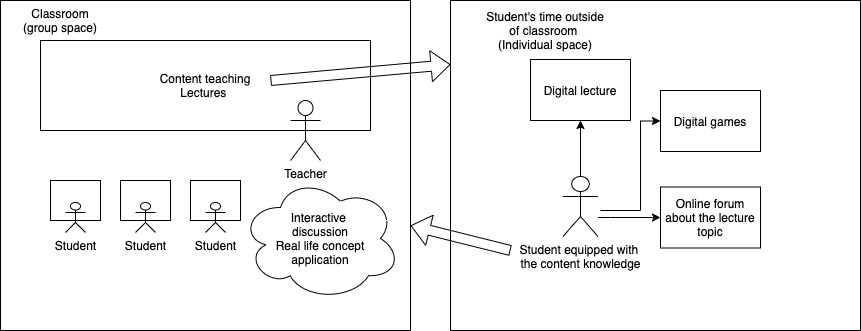 The flipped purpose of group and individual time
The flipped purpose of group and individual time
Flipped classroom is a “pedagogical approach in which direct instruction moves from the group learning space to the individual learning space, and the resulting group space is transformed into a dynamic, interactive learning environment where the educator guides students as they apply concepts and engage creatively in the subject matter" (The Flipped Learning Network, 2014)
#2. What is technology’s role?
Before we delve right into the benefits of flipped classroom, one has to ask herself:
“What is the role of technology in this radical teaching pedagogy?”
While flipped classrooms are possible without the use of digital content, we want to leverage on the ability to “create once, used a million times”. Create a good content that follows your own curriculum and many teachers can leverage of the digital resource; freeing up their classroom time for other forms of teacher-student engagements.
Some of the key benefits includes Scalability & Flexibility. Your content and your teaching can reach many more students on-demand. It can be repeated if students needs to revisit the explanation. It can be streamed and played at their own time outside of class when they feel most productive. There is flexibility in the pace students can now take to learn. There is scalability on these contents being reused.
#3. Benefits of Flipped classroom
- Students can now learn at their own pace as videos can be watched again
The lecture contents, in forms of manageable length videos, can be provided for outside of classrooms. We allow the traditional passive learning to take place outside of the classroom. This will free up time to have more meaningful engagement with the students - clarifying learning points, additional learning objectives can be accomplished through active learning.
- its more efficient, as students are more prepared to contribute in the classroom
As students are more prepared for classrooms, so are their accountability for learning. Students are charged to come for class prepared. Thus their own responsibility and accountability for their own learning is increased.
- It enriches the classroom as more time can be spent on group work and projects
When the traditional learning takes place outside of classroom time, the classroom now has the potential to turn into a workshop that incorporates and focuses on active hands on learning. With flipped classroom, active learning approach becomes the core component rather than a supplementary to the lectures.
- Doing homework in class allows students to help each other. Helping the advance and less advance learners
As the class becomes more interactive and bi-directional, suddenly we find space for students to step up. As students are now charged to help their weaker students, the classroom can starts to function like a family - or even a small society. Each with a common goal, but having different interactions and forms to teach different needs; Each students now play a responsibility of adding onto the educational experience of their peers. It feels safe, and it feels like the ideal we would like to impart
The classroom can serve as an example of what the world should look like—all students with equal power, regardless of their culture or background—rather than a replication of what it is.
- Flipped classroom allows teachers to target students who really needs help instead of those who are just confident
- Flipped classroom allows teachers to guide by the side instead of teaching at the front.
- Teachers who are not good presenters can use third-party videos to explain concepts and focus on teaching styles that best suit them such as project work or experiments. Once presented and recorded, teachers don’t have to teach the concept over and over again. They gain more time to focus on the needs of the class.
- It promotes equal learning opportunities as all kids get the same attention when doing their homework; either through the teacher or their more advanced classmates.
This includes the support for diversity in student learning styles. For example, in addition to lecture students may reflect on materials through questions and discussions with the classroom facilitators. If they are more comfortable with their peers, they can also learn by working with their classmates to solve problems, demonstrating and arguing their own solutions to class experiments and work.
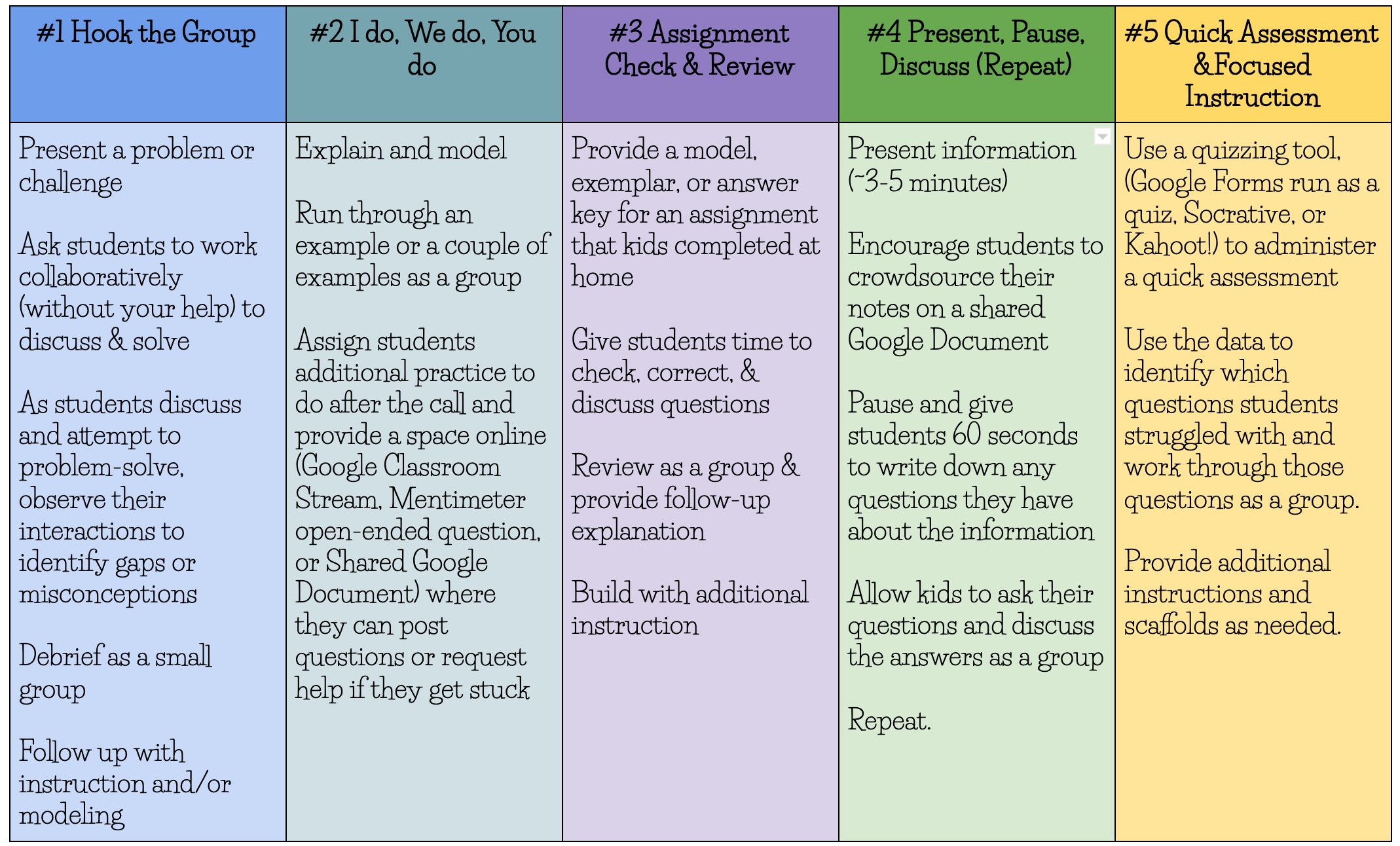
#4. How to get started?
There are many tools out there for one to leverage on. You can also reference my post of the educational tools that are available for us
1. Decide what technology you will use
I’ve also taken the time to curate a list of highly useful technology to facilitate discussions and flipped classroom’s content sharing. It can be the use of videos to do your digital lecture or it could be through the use of games. These are merely tools that allows you to put up your own content based on your own curriculum and syllabus for students. Whichever the tool, find one that is best for your use case; straight forward and easy with lowest barrier to entry.
Check out the Educational tools!
2. What video service are you going to use?
Now once you consider your technology, you have to then decide if you want to utilize a low technology or high technology approach. Low technology could mean simply just a 5mins video of you teaching the content from a particular topic. You can just upload your video on Youtube and then reference that using the video’s URL.
High technology approach will use an application that will capture both your audio and also your computer screen. This allows you to reference visual resources while you walk through the content. You can use powerpoint or basically any form of visuals that will aid your teaching.
Once you have considered this approach and have created your own video. Now you have to figure out which video service do your students have access to? Do you want your videos to be public or private.
Ultimately, the most common choice will Youtube. It is highly accessibly across devices, they have friendly UX that even toddlers are able to navigate the application even before they can talk
3. Set up your virtual class!
From the educational tools, one of the effective tool to create your class workflow is “eduflow”. It allows you to create your own segments of your class. First we will watch videos, then we will have a forum to answer a question “what have you learnt about algebra”. Now you can review your peer’s answers and check if they are correct or wrong.
Below is a screen record of my own personal trying of eduflow to create a class curriculum on space exploration!
4. Find out more information on educational technology forums
As the world evolves to embrace technology in the educational space, communities of people coming together to put together great ideas, experiences, and expertises on remote learning and flipped classroom concepts.
Listed below are some of the ed-tech forums with active communal discussions:
- Twitter edtechforum is one such platform for teachers to come together to share
- Reddit edtech There are discussions about the educational space
Below is a small guide on how to get started on your remote teaching experience for each of your class.
Here’s also an interesting Youtube video on how to get started on flipped learning as well:
#4. Challenges of Flipped classroom
Not all implementations come without its challenges. As we are showered with the benefits of flipped classroom and the amount of classroom time freed up from rogue learning and transformed into interactive discussion and application of concepts, there are still challenges that may create inertia or even stiffen teacher’s adoption of flipped classroom.
No, you’re not the only one facing these problems
1. Faculty buy-in
Since facilitators are the ones to persuade or require students to watch the online videos or complete class readings before the class. If the faculty members are not onboard to share and work upon this expectation on students, theres a good chance that students will not come prepared.
As teachers are the ones to drive such an initiative in each of their classrooms, they have to be convinced of its benefits and the time gain for more interactive discussions and concept application when the lectures and content are taught digitally outside of the class. Without the core personnel’s buy-in this entire concept will naturally not work.
2. Proper access to technology and resources
While it’s all smiles to understand the benefits to leverage on these digital resources, one has to bear in mind the vast financial backgrounds of their students. Even in developed countries where almost every student have access to basic education, not everyone are in the same economic strata and thus may not have the same access to resources such as laptops or mobile devices. It is easy to forget these people when they are hiding in plain sight amongst us.
To get around this, teachers can set up back-up plans. Students can be taught what to do if the internet goes down, or they don’t have access. This can include identifying safe spaces for accessible wifi, offering a library with computer devices to borrow or utilise, and providing learning materials on USB drives for offline learning.
3. More time spent on preparation
Content is vital to creating a successful flipped classroom. A new approach often requires fresh resources. Spare time is the one thing few teachers have in excess thus the thought of designing and creating new content can be enough to turn off the most enthusiastic teachers. This also means, some teachers that are more competent in their teaching styles to be the ones generating the digital content for all other teachers to utilize. While teachers that are more skilled in the class engagements can be the ones to anchor the classroom activities or case studies for other teachers to reference.
4. Lack of student discipline
While it is all good and beneficial to leverage on the flipped classroom concept, for students who haven’t had any exposure with flipped classroom, this setup can be a challenge. Students can struggle with self-discipline and coming to class unprepared can render the method ineffective. There can be alternatives for teachers to cope with this situation. Some ways could be either through grades allocation to constructive class participation (which requires them to know their content), or through enforcement of pre-class assignments. You can find more information in the URLs below, they are really useful.
If getting students to come to class prepared is a challenge, some may suggest to have students come into class or teacher’s consultation on their otherwise free time from recess, lunch, study period, study hall, before school or after school to do this preparatory work. Taking time off from other places can also link learning with discipline,
At the start of this section, one thing is clear. Whatever challenge you may face, you’re not the only one facing them. You are not alone. Breathe, there is no problem that cannot be solved. Here’s a video I’ve found about overcoming common challenges of flipped classrooms (:
#5. This is too tough. Any alternatives?
While flipped classroom is merely just a pedagogy, there are other alternatives to deliver your content to your students. What’s most important is to find one method that fits your use case. For example, flipped classrooms will not work if your students do not have proper access to digital devices privately or when there’s no public access to devices as well, which they will not be able to come to class prepared.
Often times, I will believe the teaching will then has to fail under group space within the classroom. I will not delve deep into this but i’ve found some articles regarding alternative teaching methods which I hope will provide some insights for teachers like you! Check it out here.
TLDR
Currently, students with caring parents, older siblings, or expensive private tutors have clear advantage over those who don’t. With Flipped classroom, teachers are now able to focus on weaker students and to enable them to catch up during class time during discussions and QnA sessions. Most importantly, Flipped classroom changes the roles for facilitators to take on more collaborative roles in teaching. Students will shoulder more personal responsibilities for their learning while given more impetus to experiment for hands on learning and experiments.
Reference:
